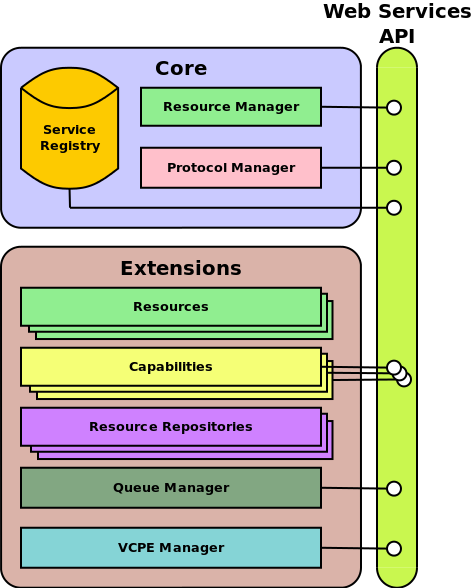
OpenNaaS works as an standalone OSGi application as is explained in Technologies. In top of it, OpenNaaS is deployed as a set of OSGi bundles. OpenNaaS architecture is divided in two parts: core and extensions. Core is the basic functionality of OpenNaaS and extensions are optional to add more features.
There are two basic components in OpenNaaS: resources and capabilities as it is detailed in System Architecture.
Core components
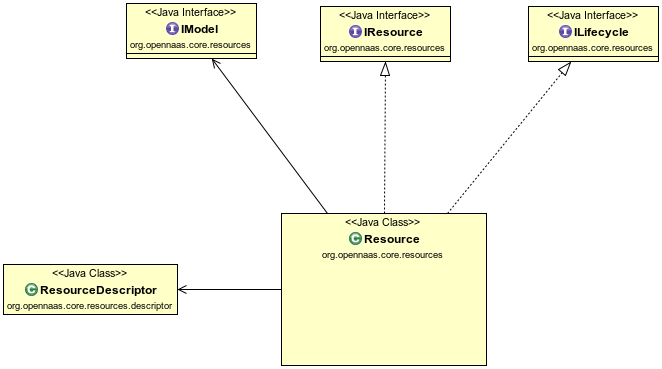
Resource
Resource Descriptor
A resource is instantiated in OpenNaaS from its Resource Descriptor, an XML file which provides the necessary parameters to configure a resource. It contains the type, the name and the capabilities of the resource.
In OpenNaaS source code, resource descriptor is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.descriptor.ResourceDescriptor Java class in org.opennaas.core.resources project.
Resource Model
The Resource Model is a description of a resource which contains all the information that OpenNaaS can access from it. It is based in the CIM specification.
In OpenNaaS source code, resource model is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.IModel Java interface in org.opennaas.core.resources project.
Resource Life cycle
Resources have a Resource Life Cycle as it is defined in System Architecture. It is defined by state diagram and its transitions.
In OpenNaaS source code, resource life cycle is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.ILifecycle Java interface in org.opennaas.core.resources project.
Finally resource can be UML modelled as:
Resource Manager
The Resource Manager uses these descriptors to instantiate each resource in OpenNaaS. Moreover it provides the interface between the user and OpenNaaS to manage resources' life cycle.
Resource Repository
The Resource Manager creates a new Resource Repository for each type of resource. Each repository has the responsibility of managing resources of a concrete type. The Resource Manager interacts with each repository.
In OpenNaaS source code, resource repository is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.IResourceRepository Java interface and implemented by org.opennaas.core.resources.ResourceRepository Java class in org.opennaas.core.resources project.
Capability
A Capability represents a feature or an ability which a resource can do. Each resource's type has a set of capabilities which define its features.
In OpenNaaS source code, capability is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.capability.ICapability Java interface in org.opennaas.core.resources project. Each concrete capability implements this Java class defining its own implementation.
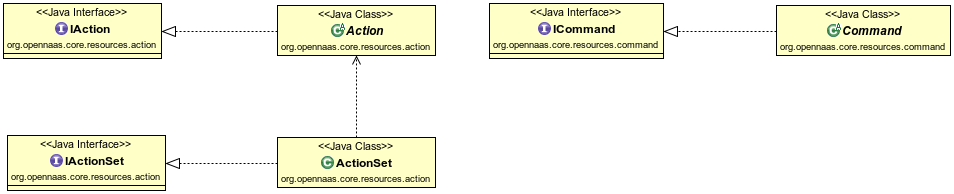
Action Set, Action and Command
Each capability has an Action Set that contains actions. An Action is used to send operations to a specific device associated with a resource. The action set implementation depends on type, model and protocol to access of each resource. A Command is each atomic operation which an action can be divided.
In OpenNaaS source code, action is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.action.IAction Java interface and implemented by org.opennaas.core.resources.action.Action Java class in org.opennaas.core.resources project. In the same project, action set is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.action.IActionSet Java interface and implemented by org.opennaas.core.resources.action.IActionSet Java class. Finally, in the same project, command is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.command.ICommand Java interface and implemented by org.opennaas.core.resources.command.Command Java class.
Finally action can be UML modelled as:
Queue Manager
The Queue Manager is mandatory capability of each resource. It is a transaction execution engine (sometimes simply misnamed queue) that queues actions and executes them. If anything goes wrong, the operation is rolled back. It has an state diagram defined by four states:
- Prepare
Starting state where working configuration is saved as a backup. - Execute
Next state where each action is executed sequentially. - Commit
If all actions are correctly executed, all the changes are committed and backup configuration is discarded. - Rollback
Opposite to commit state that becomes when an error is produced during execute state. The backup configuration is restored.
In OpenNaaS source code, queue manager is defined by org.opennaas.extensions.queuemanager.IQueueManagerCapability Java interface which defines the capability itself and implemented by org.opennaas.extensions.queuemanager.QueueManager in queuemanager extension project.
Protocol Manager and Protocol Session Manager
OpenNaaS uses lots of different protocols in its operations. The Protocol Manager copes with each protocol and session. A Protocol Session Manager is instantiated for each session established with each concrete device. The user can interact with OpenNaaS creating, removing, editing or getting information of each session and protocol.
In OpenNaaS source code, protocol manager is defined by org.opennaas.core.resources.protocol.IProtocolManager Java interface and implemented by org.opennaas.core.protocols.sessionmanager.ProtocolManager Java class in org.opennaas.core.resources project. In the same project, protocol session manager is defined by
Extension components
Each resource type and concrete capability are developed as extensions of OpenNaaS. In current OpenNaaS development, there are a set of resources, each of them has one ore more capabilities with zero or one driver developed. More information can be found in Compatibility Matrix.
Router
The router resource is the most used resource in OpenNaaS, it represents a router device with some capabilities.
BoD
TODO
Optical Switch
TODO
Mac Bridge
TODO
Network
TODO
VCPE
TODO
------------------
- Resources: Router Junos 10.10, BoD AutoBAHN, Optical Switch W-onesys, Mac Bridge Resource IOS, VCPE, Network
- Capabilities: Obligatòria (Queue), BoD (L2BoD), (VLAN-aware Bridge), (ROADM connections, ROADM monitoring), (OSPF, BGP, Chassis, GRE Tunnel, IP, Static Route, VRRP)
--------------
Finally, OpenNaaS can be summarized in this module diagram: