Overall architecture and components
Mantychore OpenNaaS is implemented with the OSGi specification and works with Fuse Service Mix 4.34. Fuse works as a Service platform which implements the OSGi specification. It provides a set of libraries and tools to allow easier development of Fuse components.
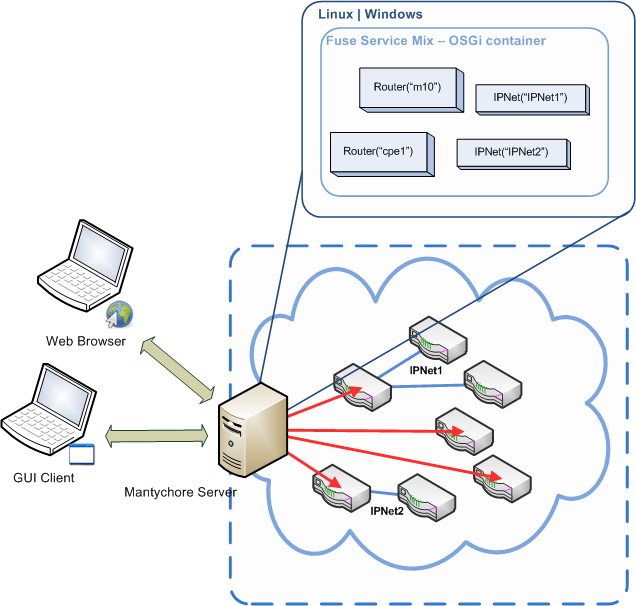
The This figure show shows a typical architecture.
The picture shows how a Mantychore an OpenNaaS user connect connects to the Server and how Mantychore OpenNaaS connects with its the devices it manages.
The Mantychore OpenNaaS software is multiplatform. To set up a Mantychore an OpenNaaS architecture, you need:
- A Computer which it is going to act as a Server. It will 'll have Fuse Service Mix installed, along with the the Mantychore the OpenNaaS components.
- Configure SSH to enable setup that allows access to the routers (see compatible devices).
There are two types of Mantychore of OpenNaaS client:
- GUI Client. A desktop program has implemented with RCP.
- Web site. With Through Ajax and and RAP, it is implemented a site which simulates the GUI client.
Internal architecture
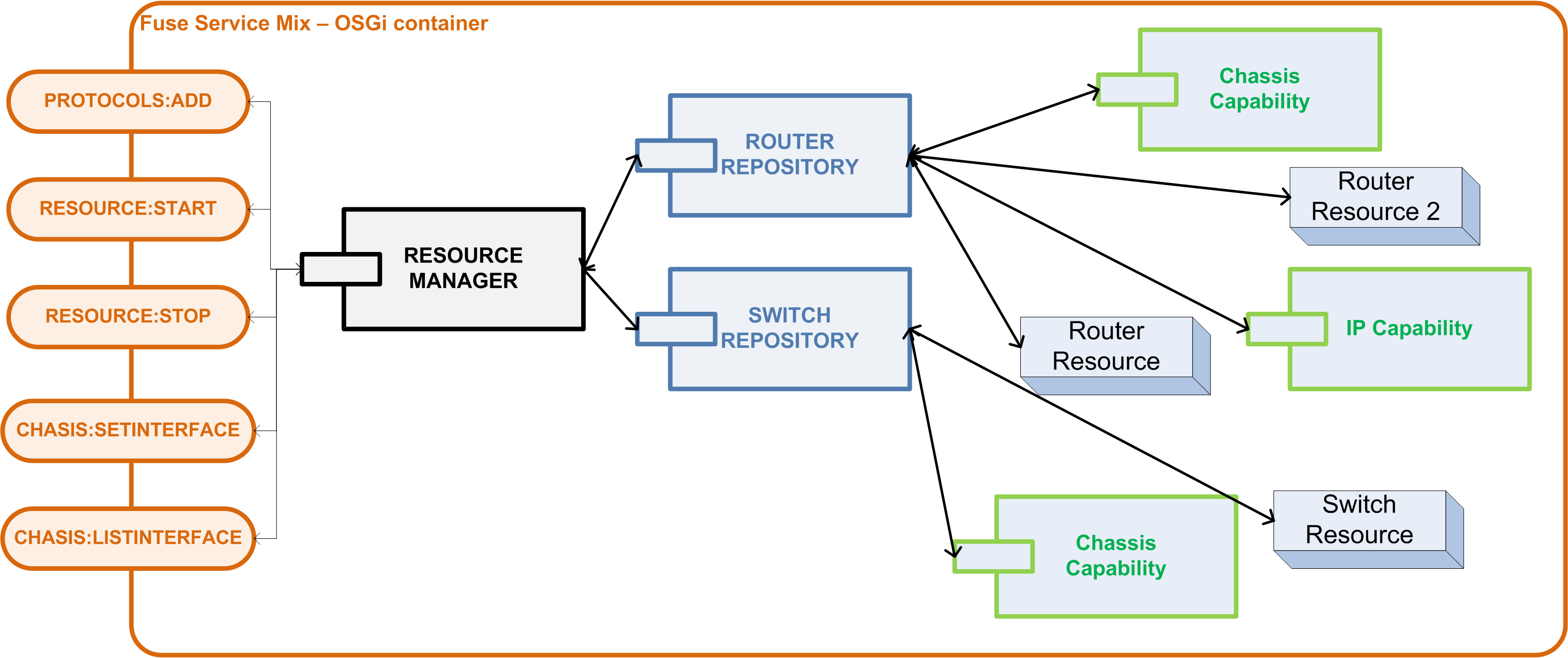
At present, the Mantychore the OpenNaaS software is implemented on top of an architecture where it exists two main actors arebased around two core components: resources and capabilities. With these components, Mantychore OpenNaaS can describe all the necessary virtual resources (a resource component). Resources contain the information (model) that represents itself and capability, which represents its features (a capability component).
In order to help to manage the resources and their capabilities, also, there are other components to provide other necessary required features: SessionManager, Protocol, Model, ActionSets, ResourceManager, etc ...
ResourceManager, ResourceRepositories and Resources
A resource and its capabilities are registered in different resource repositories as their type. For example, a router resource will have its repository and a switch resource will have another different. Consequently, any new switch resource will be registered in the same repository that the other switch.
OpenNaaS supports different types of resources (switch, routers, ...). In order to organise them, OpenNaaS can implement different kinds of repositories that group the resources according to their type. The resource repositories manage the resources created within the platform, it also allows persistence into the database. To allow OpenNaaS to support new resource types creating a new repository is needed for the new ones.
The feature set provided by a resource is represented through capabilities. Each capability must be associated to a specific type of resource according to functionalities their provide. For example, a BGP police is a feature of routers, thus the BGP capability has to be associated to The different capabilities are associated with a specified type (a BGP capability is associated with a router resource, but the same capability has not doesn't make sense with switches because a switch this resource type resource cannot configure BGP policies) are registered in the correct repository..
Since there will be a resource repository for each type of resource, it's necessary to have a global component to manage the different repositories. The ResourceManager will be in charge of this task. It will offer a set of actions to control the repositories and its resources. Finally, it is necessary a manager to the repositories and resources. Consequently, it will have to manage the management of resources, its persistence support, loading of configurations and other management tasks. Mantychore has implemented a ResourceManager where it will be responsible of all these actions.
Resource Descriptor
For the creation of a resource, the ResourceManager uses a description file (ResourceDescriptor) which provides the necessary parameters to configure a resource. For example, it contains the type, features name and the capabilities which our that the resource supports. An example:Here an example of a resource descriptor is provided.
| Code Block |
|---|
<resourceDescriptor>
<!-- Capability information. It specifies device model and version -->
<capabilityDescriptors>
<capabilityProperty value="junos" name="actionset.name"/>
<capabilityProperty value="10.10" name="actionset.version"/>
<information><type>chassis</type></information>
</capabilityDescriptors>
<!-- Queue capability information. It specifies device model and version. IT IS OBLIGATORY -->
<capabilityDescriptors>
<capabilityProperty value="junos" name="actionset.name"/>
<capabilityProperty value="10.10" name="actionset.version" />
<information><type>queue</type></information>
</capabilityDescriptors>
<!-- Resource information. It specify type and name-->
<information>
<type>router</type>
<name>junos20</name>
</information>
<properties/>
</resourceDescriptor>
|
Model
...
Resource
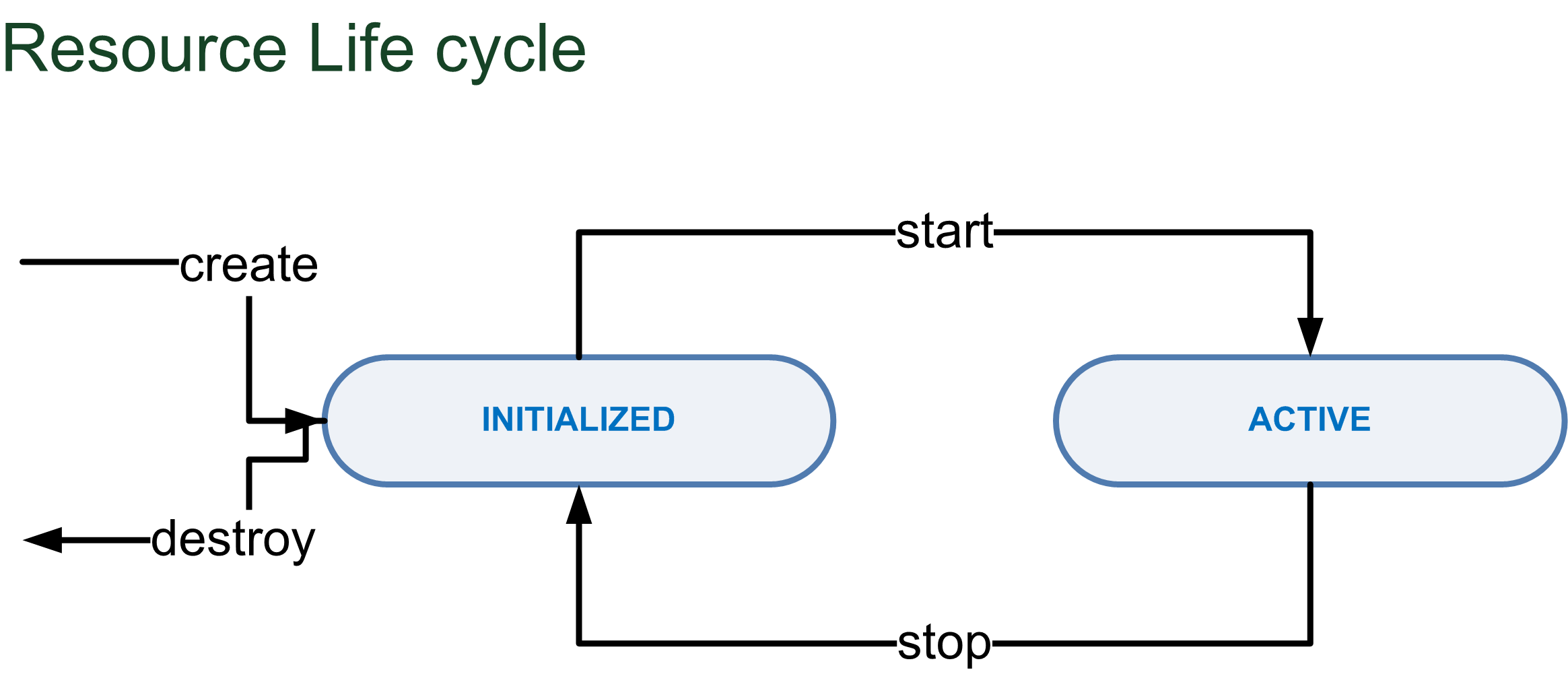
A resource is the logical representation of a physical or virtual resource representationdevice. It was As explained that it contains the information (model) and features (capabilities) which it can use. These parameters have to created and started to be an active resource. In this picture is possible to see the resource life cycle:
The end user do these state movements via the Mantychore server console
necessary to allow OpenNaaS to work with the device. To create a resource within the OpenNaaS platform a well defined life cycle is required.
The next figure represents the resource life cycle. First of all, the resource must be created. This action concludes leaving an initialized resource in the platform. In this state the resource can show information of its features and the protocol context can be set. At this point, starting the resource will activate its features and allow the execution of actions on it.
Using the commands provided by the OpenNaaS server console, the user can control the state of the resource. The following table lists the possible commands and their actions. The initial state indicates the state from which the command can run, while the final state indicates the state that the command induces.
Resource Command | Actions | Initial State | Final State |
| INITIALIZED | ACTIVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
create | - read resource descriptor | No resource | INITIALIZED | |||
start | - get capabilities | INITIALIZED | ACTIVE | |||
stop | - reset capabilities | ACTIVE | INITIALIZED | |||
remove destroy | - delete resource descriptor from the database | INITIALIZED not | yet No resource |
Capability
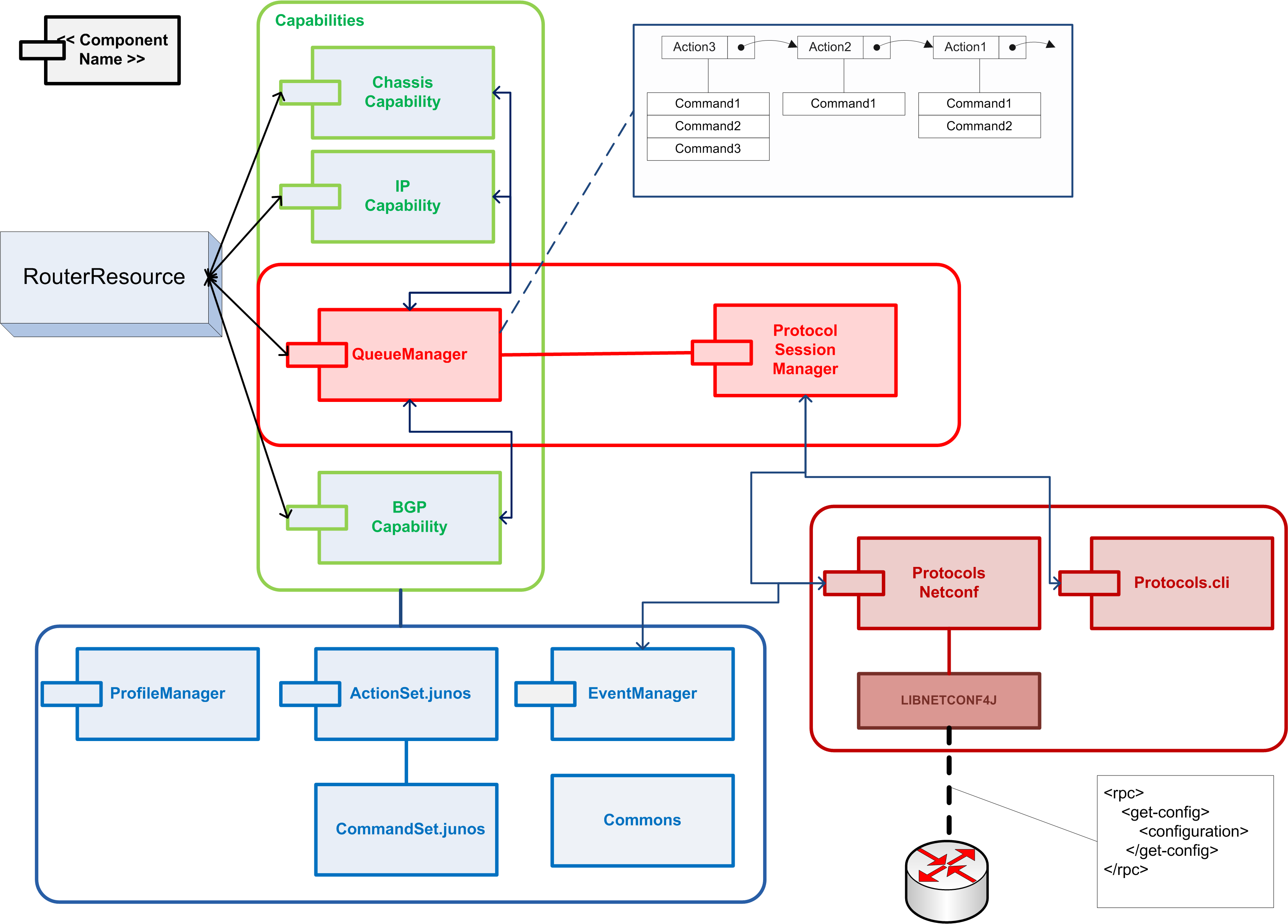
Architecture picture overview
Model
When a resource is initialized and started, it needs a component which maps the resource description. This description is all the information which OpenNaaS can access from the resource. For this purpose, OpenNaaS has a model component (based in the CIM specification) which loads all this information.
Capability
OpenNaaS Mantychore links a set of capabilities to a resource where each capability represents a new feature or ability which a resource can do. For example, a router resource will be able to have capabilities related with operations for the 1, 2 and 3 level network. However, a switch resource will only be able to use capabilities for the 1 and 2 level network.
Each capability have has a list set of actions (this set is named ActionSet) where are , used to send operations to a device. Each of these actions is implemented for a device and a protocol context which understand understands the operation.
Finally, it exists there's a mandatory capability for all the resources, the queue capability, which its main functionality is the management of the actions which are sent to a physical device.
The definition of an ActionSet, QueueManager and its functionality will be explained better in the next issue.
Architecture picture overview
ActionSet component
The ActionSet contains the implementation of the operations which a capability can send , called Actions, that can be sent to a device. For this reason, this the ActionSet , implementation will depend of on the model , and type of the resource and on the protocol to access . Each action is to the resource. The Actions belonging to the same ActionSet are implemented for a device with these parameters. Each action is consist of commands with are atomic operations which can be executedspecific device following this criteria (model, type and protocol). Each Action can be broken in different atomic operations, called Commands, which perform the action once run on the device.
ProfileManager component
The profile manager provides the functionality to overwrite configured actions. This feature permits to the allows end users personalize to customize their actions which i can be adapted for in order to adapt them to their use cases.
The ProfileManager is implemented as a bundle which is listening continually, waiting some new profile to register in its list of profiles. When this profile is registered, this profile will be able to be Action customization is done via Profiles. A Profile is a end user provided bundle containing an implementation for some OpenNaaS configured actions. Profiles may be linked to a set of resources. Then, meaning that when a resource wants is to execute some an action of a capability, first, it will check if its profile contains some overwritten action for this action and capabilityits profile is first checked for an implementation of that action.
ProfileManager stores loaded profiles and manages their lifecycle. It is implemented as a bundle which is continually listening for new profiles and registers them upon arrival. Registered profiles are then able to be linked to resources (with the restriction that a resource can be linked to only one profile).The resource descriptor must indicate, through the field <profileId>, the name of the profile that will be associated to the resource.
QueueManager component
This component is responsible of the execution of each action. It implements a queue and a list of operations to manage it. FurthemoreFurthermore, the queue implements a workflow where it is possible to restore the las correct last working configuration if some operations did not work correctly. Before that execute a list the Prior to the execution of the list of actions, the queue was goes in the PREPARE state, where it the working configuration is saved the configuration. After that, it starts to execute each queued action (EXECUTE state) while these actions are executed it can be two different cases. If all it was actions are executed correctly, the queue commits all the changes and discards then backup configuration (COMMIT state) and if it happened some error it restored the . If, on the contrary, some error happens during execution, the queue restores the backup configuration in the ROLLBACK state.
...
The SessionManager controls the protocol components and provides connectivity to the different devices. The SessionManager It searches available protocols among all services to register all the available protocols and when , registers them, and serves registered protocols' sessions upon request. eg: When the QueueManager needs to connect with some device, it requests to asks the SessionManager, which search searches among its configured protocol session, sessions a correct proper session to connect.
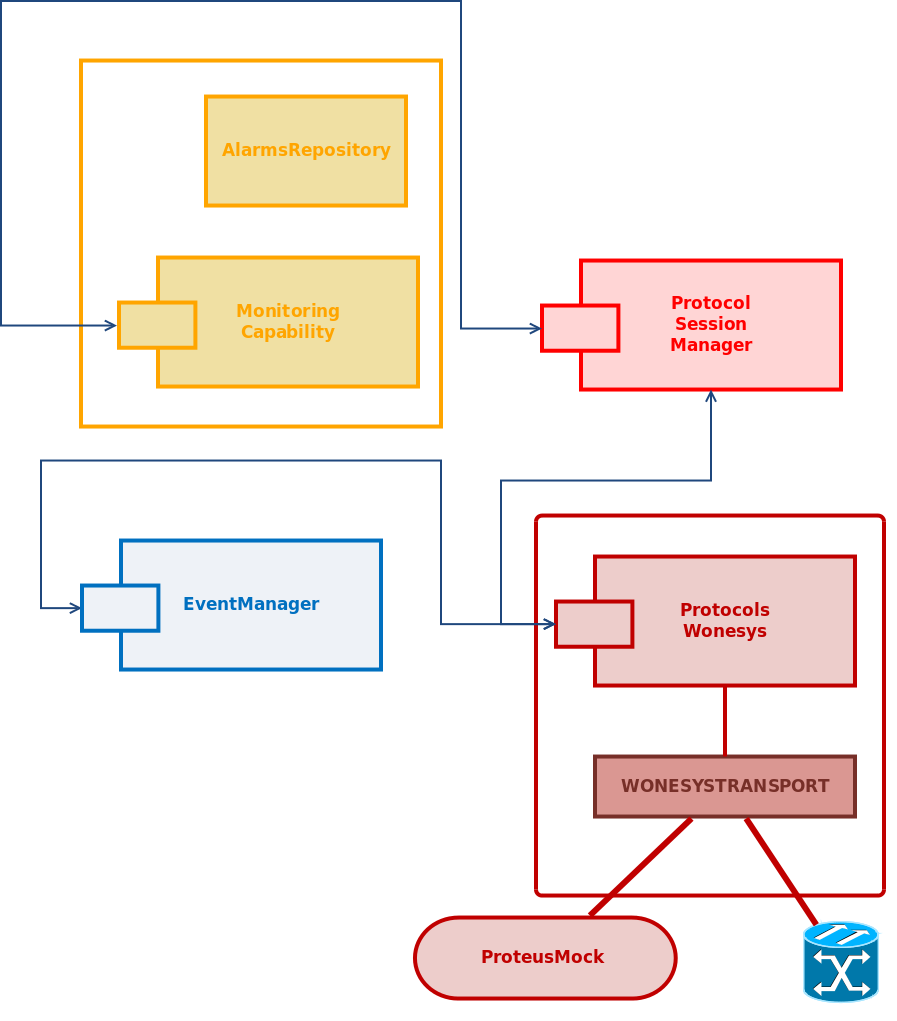
Event manager component
The Event Manager is a Karaf service which OpenNaaS uses to communicate the components. It provides an Event Notify-Listener service which is used to implement the alarm management in the Luminis module. This is an example about how this alarm management works for optical switches.
- The EventManager provides its methods to the ProtocolWonesys and ProtocolSessionManager
- The Protocol Wonesys events are listened for the ProtocolSessionManager
- The ProtocolSessionManager converts these events to Capability Alarms which is registered in the AlarmRepository
- The Monitoring Capability provides Karaf commands to control the Alarm Repository service
Protocols Used
Protocols
Here These are listed the OpenNaaS main protocols used to configure and manage the network via the Mantychore tool.
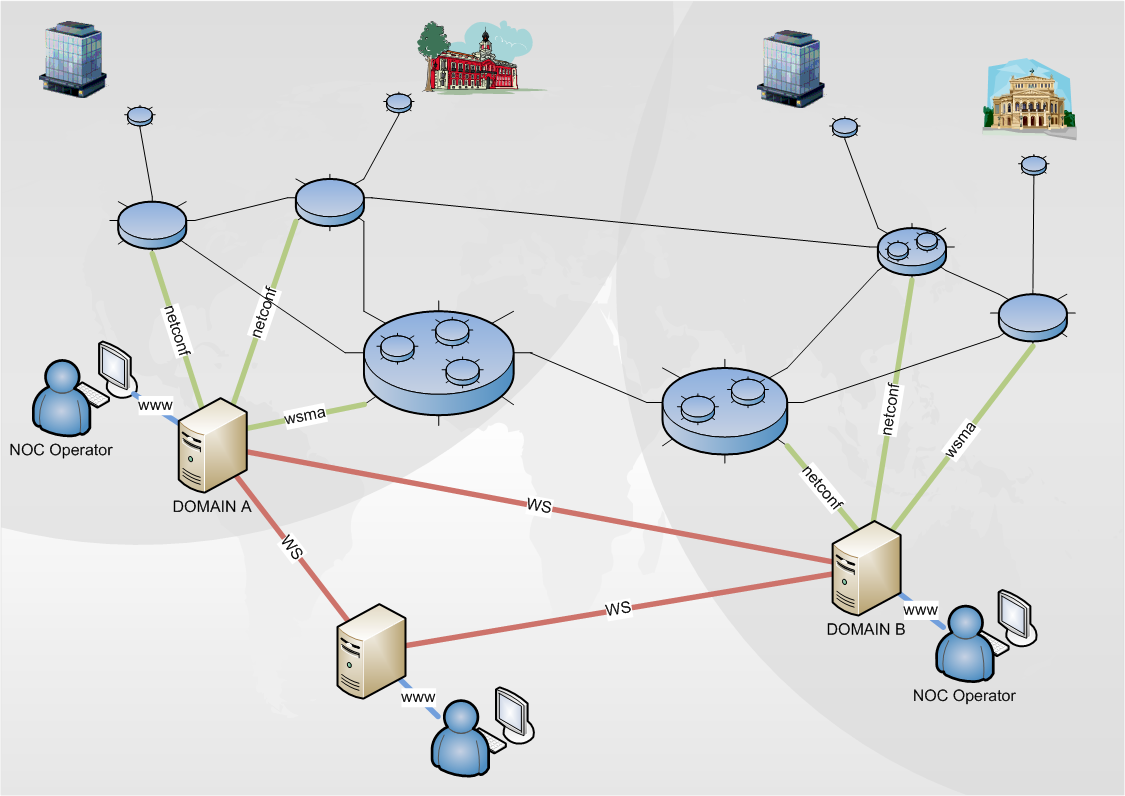
- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) - http://www.w3.org/Protocols/
- WS (Web Service) - http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/ws_intro.asp
- NETCONF - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NETCONF http://www.ops.ietf.org/netconf/
- WSMA (Web Services Management Agent) - http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/netmgmt/configuration/guide/nm_cfg_wsma_ps6441_TSD_Products_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
In the image, we can see the different protocols involved in a Mantychore OpenNaaS architecture can be seen. The green lines represent the communications to the devices.The red lines represent communication among servers, GUI and Mantychore OpenNaaS software.
Workflow
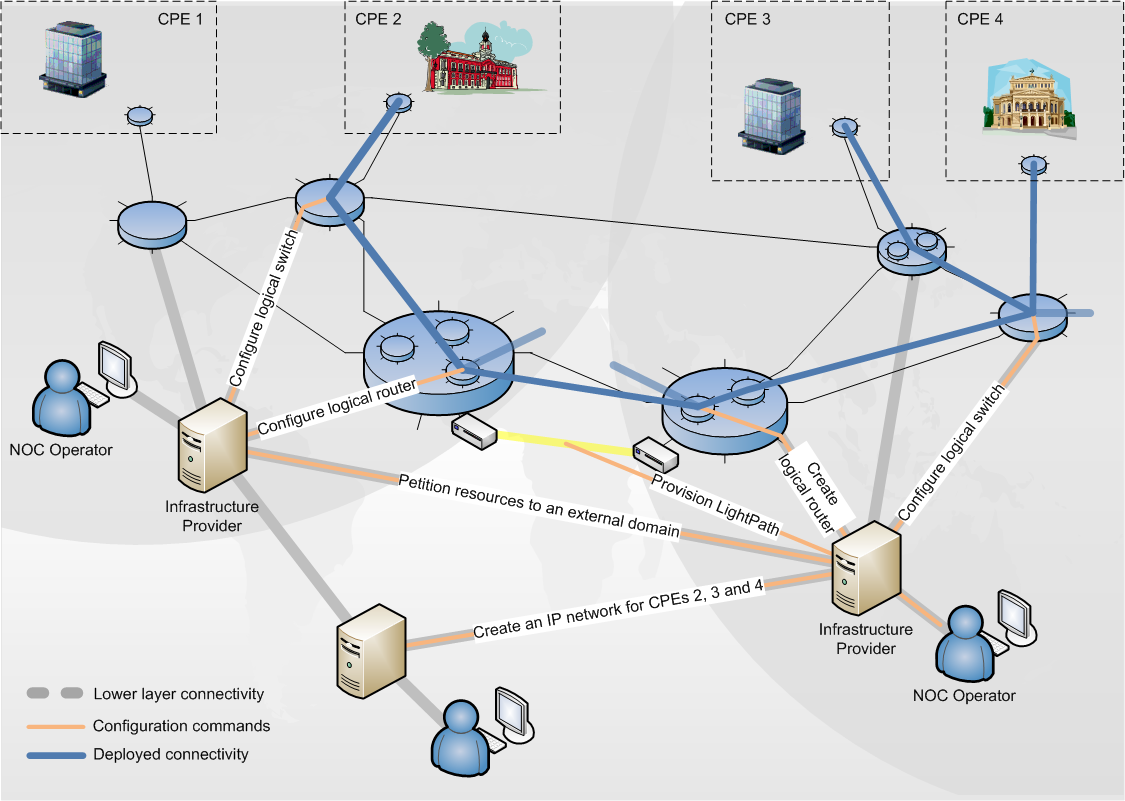
This image presents a possible infrastructure configured using MantychoreOpenNaaS. It shows where Mantychore OpenNaaS works (brown lines) to connect two public entities. In this case, Mantychore OpenNaaS does not have complete control and it works above an external infrastructure.